We recently suffered a power outage, or power cut as we prefer to call such things here in the UK. This wasn’t any old power outage either. Let me explain.
The lights went out at 17:44 on Friday April 11th 2014. I hurriedly powered down everything in the lab and office except my laptop and our broadband router, which was by then being powered from the battery in an uninterruptible power supply. When the lights hadn’t come back on a few minutes later I telephoned our local Distribution Network Operator (DNO for short), Western Power Distribution, to enquire what the problem was, and when it might be fixed. WPD’s automated system suggested that our power should be restored by about 21:00 that evening.
9 o’clock came and went, by which time the batteries in my laptop and UPS were flat. I called WPD again, to be informed that the latest estimate for the time at which I would be able to get connected to the internet once again would be 01:00 on Saturday morning. I figured I’d allow WPD a bit of leeway, and eventually went to bed having set the alarm on my smartphone for 02:00. The alarm went off, but the lights still hadn’t come back on. I phoned Western Power again to be informed that things should be back to normal in an hour or so. Bleary eyed I returned to bed.
When I arose next morning I wasn’t in need of any lights, but my router and laptop were working once again. There was, however, the continuous drone of an engine audible not too far away so I set out to investigate by following the sound, and here is what I discovered:

Diesel generator on the track to Haldon Belvedere on April 12th 2014
Another call to Western Power Distribution elicited some further information. I managed to speak to WPD’s standby manager for the day, who explained what had happened the previous evening. Initally over 300 properties had been without electricity following the operation of an automatic circuit recloser mounted on pole NLT1M in Alphington, as shown at the top right of the map of WPD’s network below (click the image for a larger version), and in this photo I took subsequently:
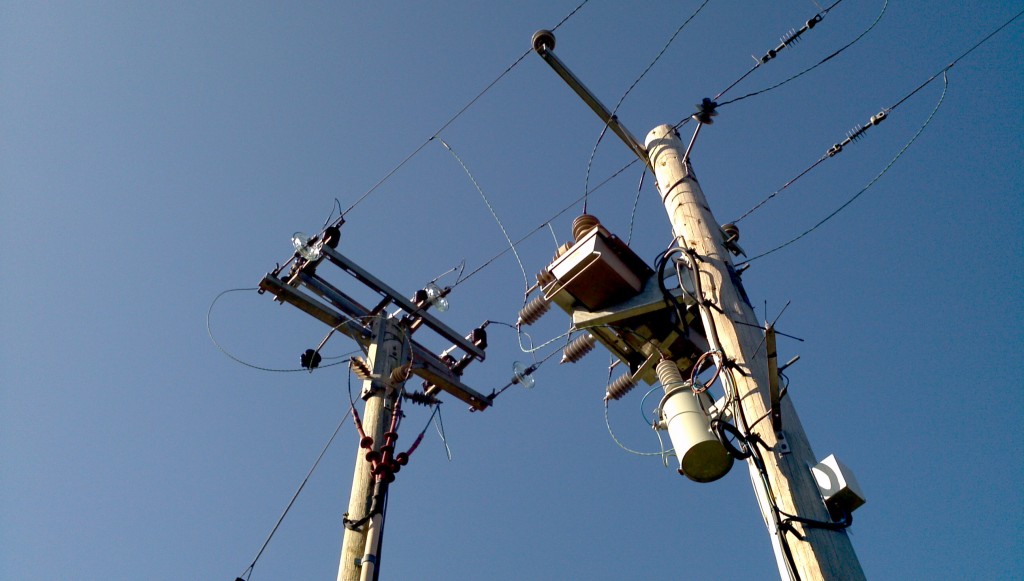

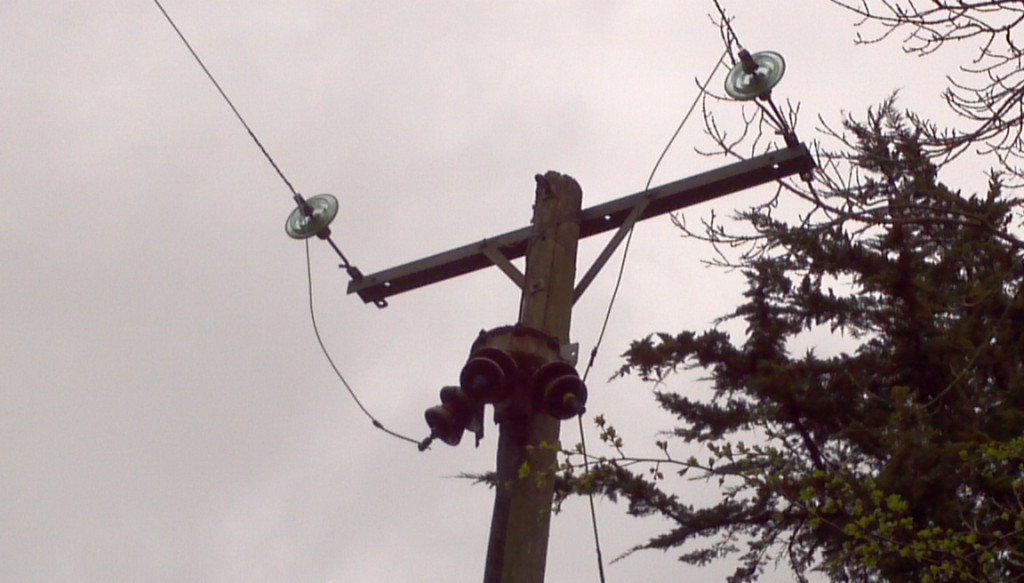
Schneider U-Series pole mounted recloser and an air break isolator in Alphington
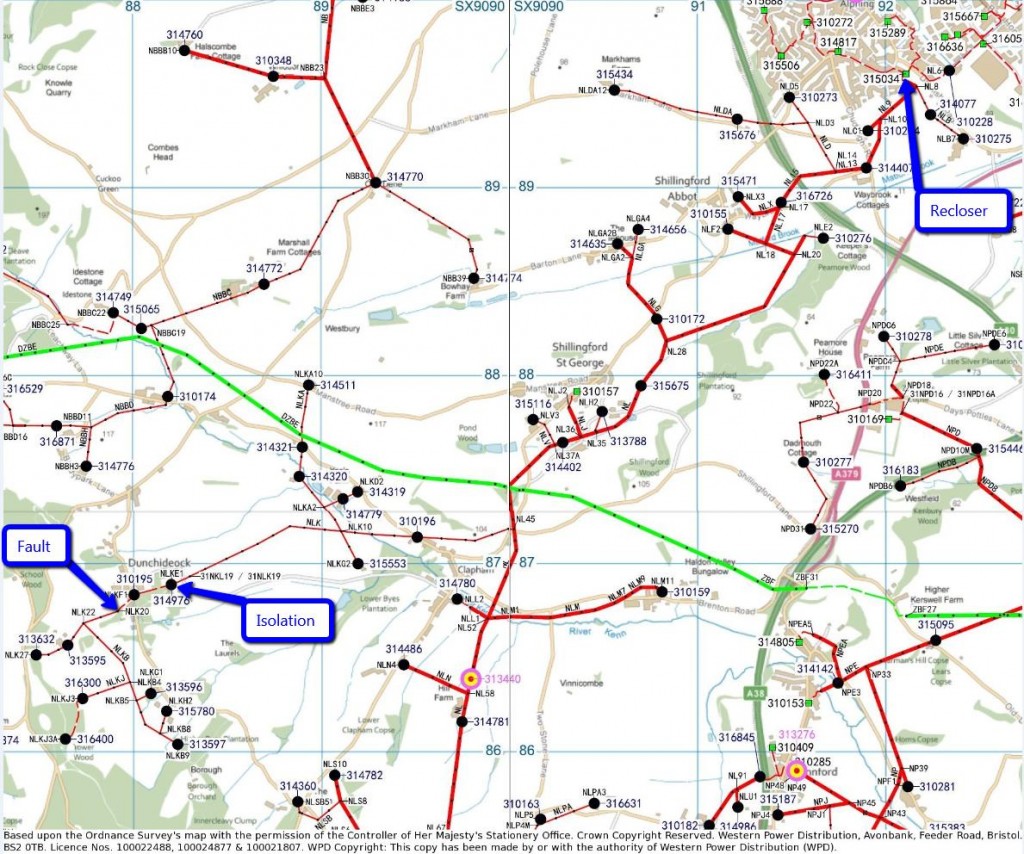
WPD map of 11 kV (red) and 33 kV (green) cables south west of Exeter
At that point everything powered via the 11 kV 3 phase (thick red) cables running from top right to bottom left of WPD’s map was without electricity. By around 21:00 the problem had been isolated to somewhere in the bottom left corner of the map, and power now reached as far as pole NLK19, near the north east corner of The Lord Haldon Hotel car park.
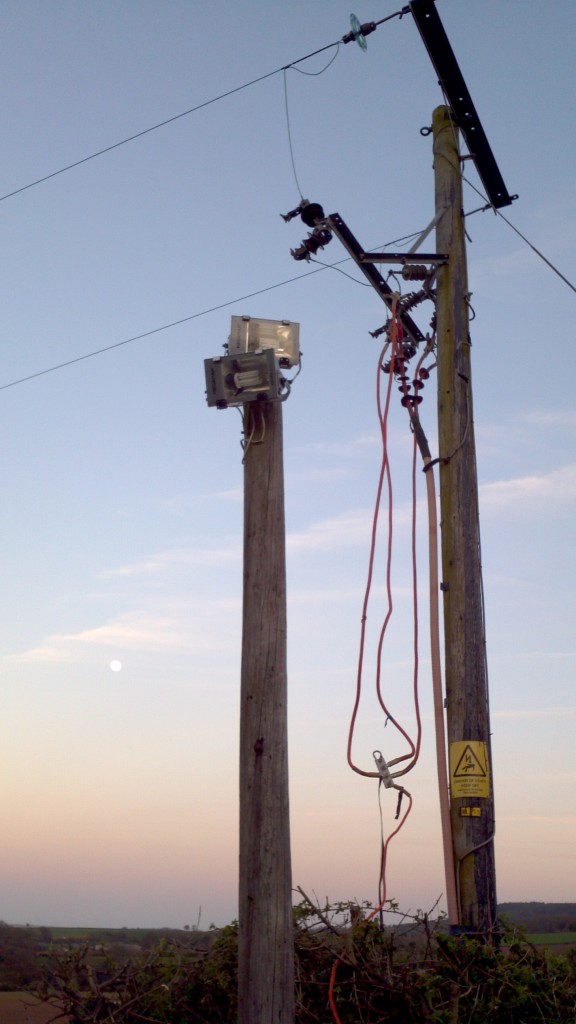

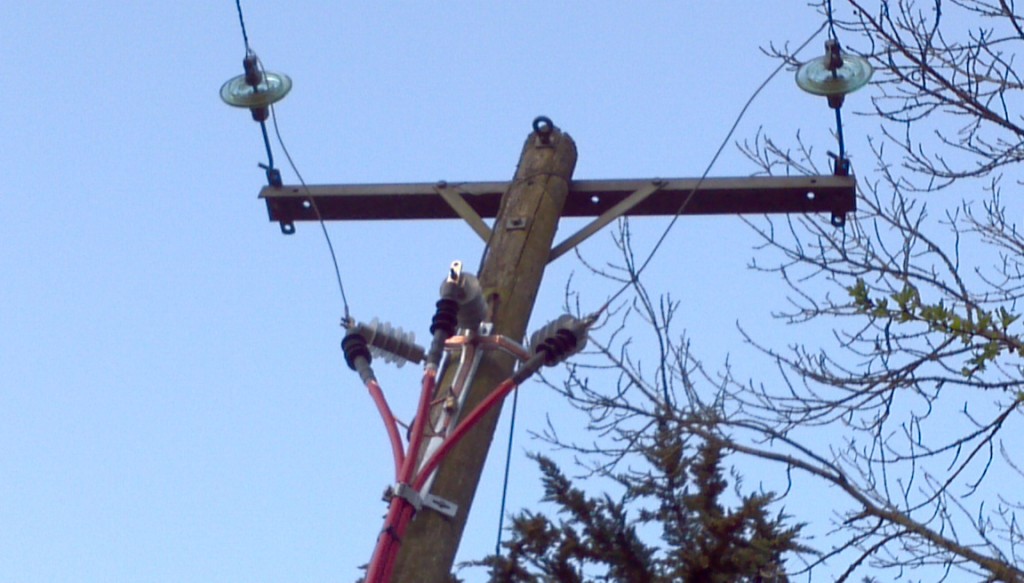
Pole 31NLK19, draped with extra cables, whilst The Lord Haldon Hotel and The Haldon Belvedere were running from WPD generators
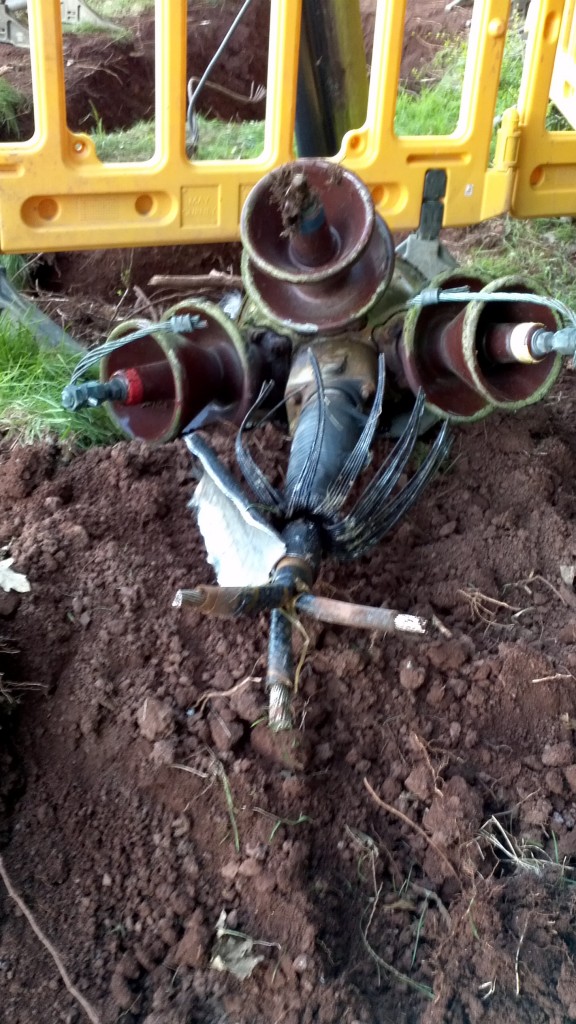
Unfortunately the hotel itself, which had a wedding reception booked that night, and everyone else in our corner of the village of Dunchideock and Haldon Hill were still without power, and WPD still didn’t know where the fault was. I am assured by a local resident that once it had got dark his wife noticed some arcing at the top of an electricity pole in a field behind his house, so he drove to the hotel car park and informed the WPD engineers gathered there about her discovery. The problem ultimately proved to be a faulty pole top cable termination, shown below in situ together with some inquisitive lambs:
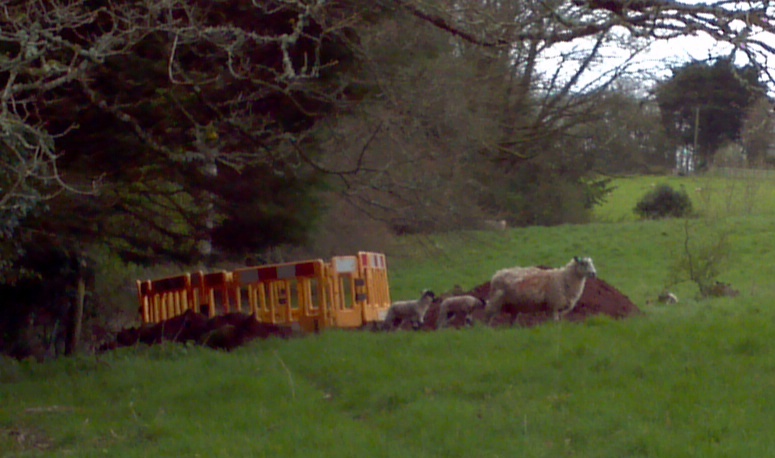


Some youthful interest is shown in a big hole in the ground
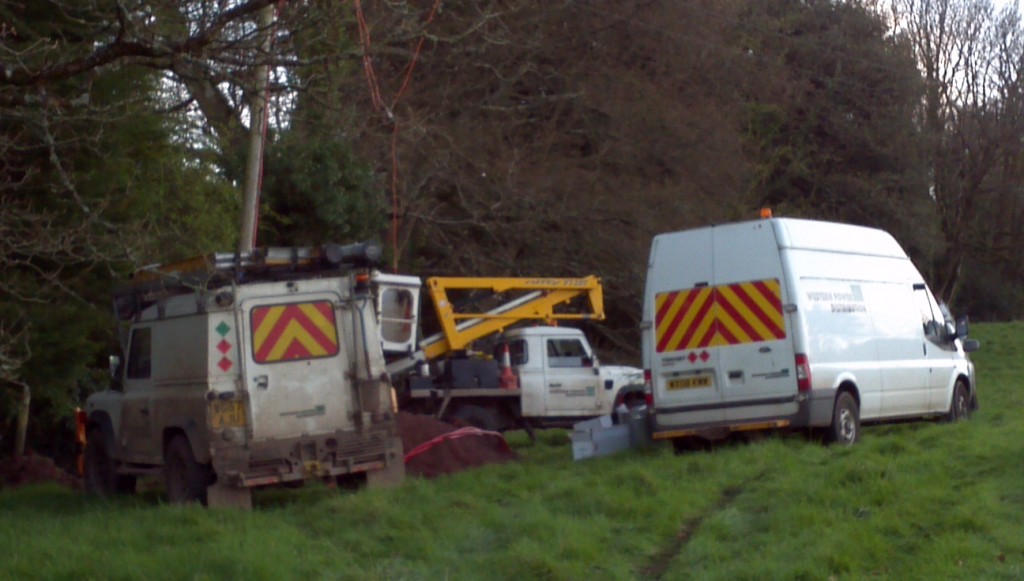
By the time the likelihood that this was indeed the ultimate cause of the problem had been established time was pressing. According to WPD they have a self imposed 12 hour time limit on turning the power back on after any interruption in supply, and there was no way this problem would be fixed within that timeframe. That being the case some generators would be required, which presented WPD with another big headache. It seems there had been some other problems in Devon on the same day, and there weren’t enough generators in Exeter to go around, so WPD brought some more in from Torbay. That still wasn’t adequate for the scale of the problem, so they brought some more in from Taunton. Even that wasn’t sufficient, so finally they had to hire a few more from Bristol, one of which was emitting the dulcet tones that greeted me on Saturday morning. Here’s one of WPD’s own generators, that was located a bit further up the road near the entrance to the hotel:
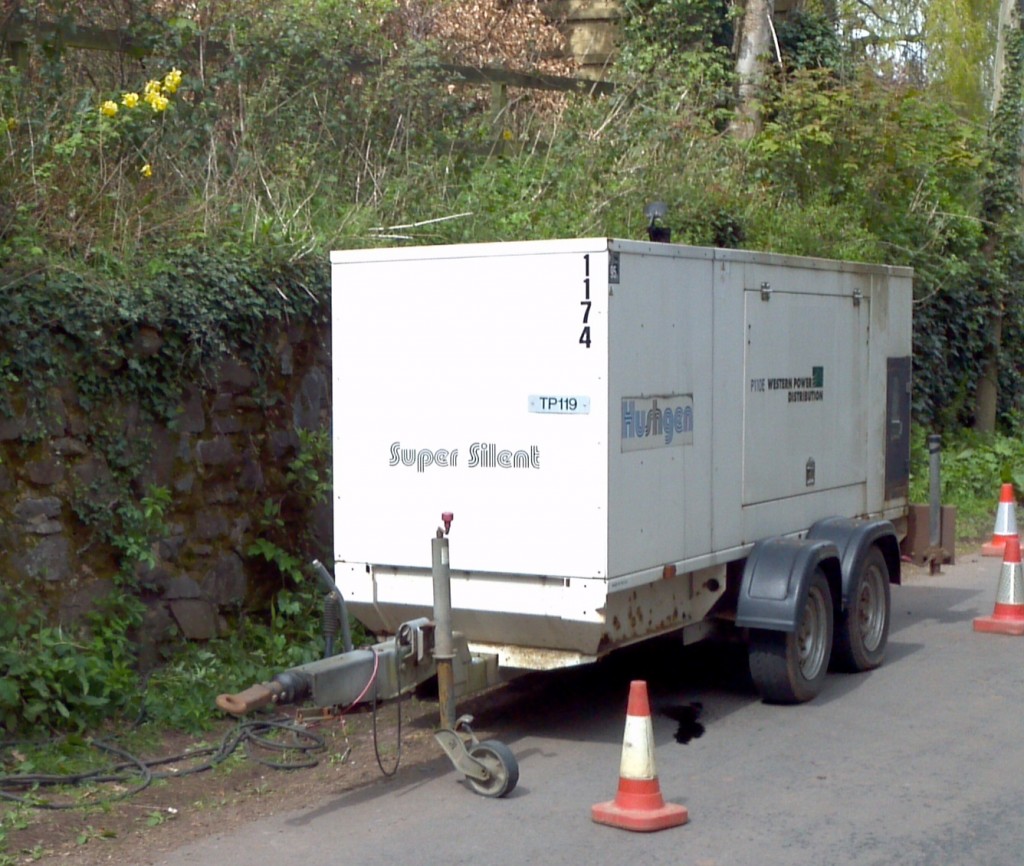

WPD diesel generator hard at work outside Pen Hill Cottage
All in all, by the time everyone affected had their electricity supply restored, which in our case seems to have been at around 3:30 on Saturday morning, 9 diesel generators were scattered across the north side and ridge of Haldon Hill. WPD assured me there was no danger of any further power cuts, since every 12 hours or so they would be hauling a bowser around the local vicinity to top up the tanks of any generator that might be running low on diesel fuel.
Whilst they didn’t have such a thing last time I checked, during the recent winter storms, I was also informed that Western Power now provide an online power cut map. This is how it looked on the morning of Saturday April 12th 2014:
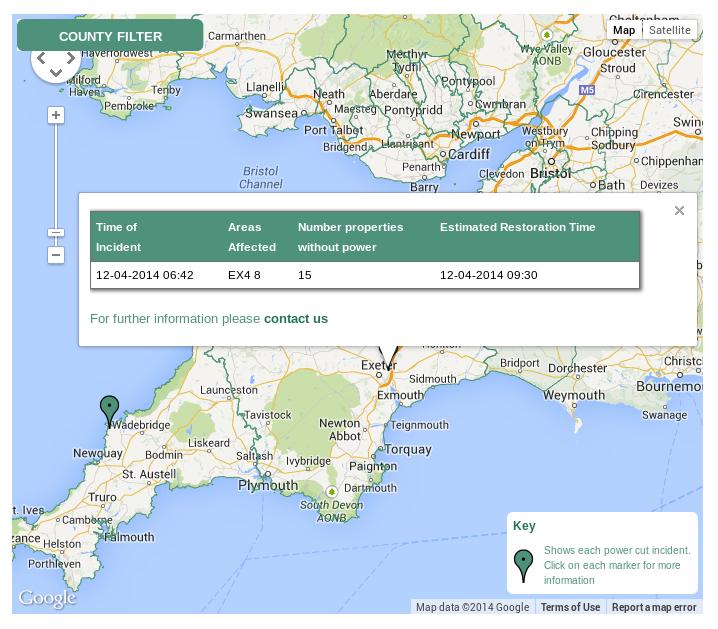
Western Power Distribution power cut map at 08:39 BST on Saturday April 12th
It seems as though “running off a generator” doesn’t count as a “power cut”, because Dunchideock isn’t on that map, all of which meant that WPD could now fix the problem as and when time permitted. Here’s how things were looking by Sunday evening:
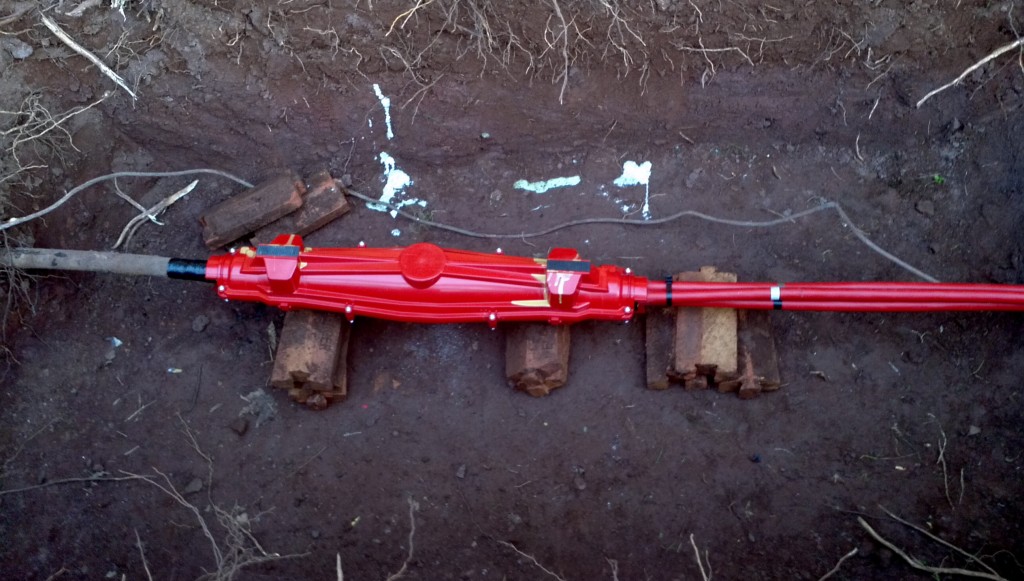




By Monday morning the epoxy resin in the Lovink red box had set, the big hole in the ground was filled in, and we were all back on mains power once again. All of which raises a few questions, in my mind at least.
In my conversations with WPD’s duty engineers I enquired whether this particular failure might be in any way attributable to the recent wet and windy winter weather here in South West England I alluded to earlier. I was told that while a causal link with any single failure was impossible to establish, it was conceivable that WPD’s electricity distribution network had suffered additional “stress” due to increased lightning strikes and the potential for trees to be more easily toppled by strong winds whilst their roots were sitting in sodden soil. I also idly enquired about the stresses placed on the network by renewable generation in the South West, but that story will require an article of its own at the very least.
In the meantime I’ve been pondering how this saga would have panned out if some of the homes in Dunchideock had already been in possession of an electric vehicle and some vehicle to home or even vehicle to grid technology. Since the powers that be here in the UK don’t seem to be wild about either of those concepts maybe a pile of shiny new lithium ion batteries from Tesla in the corner of each garage in Dunchideock might be more realistic to speculate about, or at the very least some second user EV batteries that are at least receiving some R&D funding on this side of the Atlantic? In that case perhaps we should add distributed storage to grid (or S2G for short) to our list of TLAs under consideration?
The lights wouldn’t have gone out in any V2H or storage equipped home. Their broadband would have kept on working too, so information about the failure could have been swiftly despatched to WPD’s control centre to enable the location of the fault to be pinpointed more swiftly. If some people had V2G and/or S2G installed as well, and subject to being suitably reimbursed for their public spiritedness, they could have kept their neighbours’ lights on as well as their own provided that WPD’s equipment was capable of sectionalising their network with greater granularity than at present. As luck would have it there is a pile of such equipment already in Dunchideock, although it’s only in the V2G lab at the moment rather than attached to any of the WPD poles I’ve mentioned apart from the one in Alphington, or in the corner of anyone else’s garage in Dunchideock. Here’s what a remote terminal unit looks like from the outside:
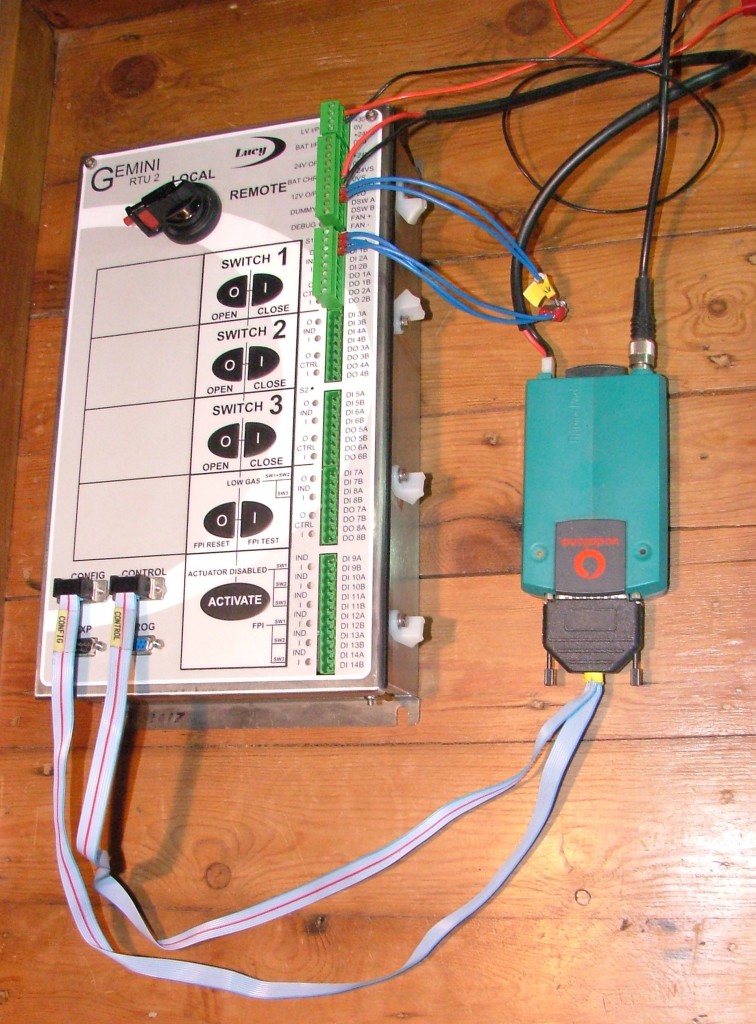
A Lucy Switchgear Gemini Remote Terminal Unit plus PakNet PAD
and here’s what the ARM powered CPU board on the inside looks like:
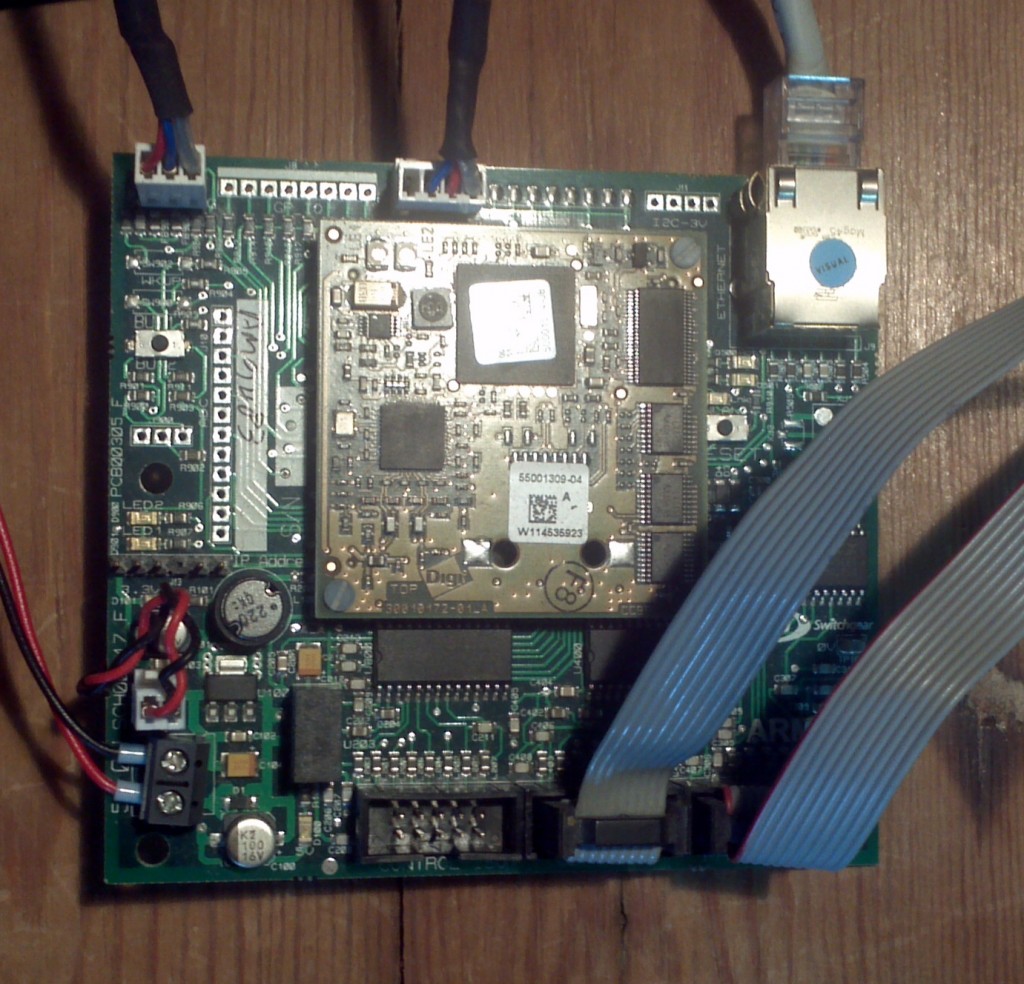
A Lucy Switchgear Gemini ARM CPU card, connected to the internet
As you can see, in actual fact it’s not a whole lot different to a Raspberry Pi, or the guts of the average smartphone for that matter:
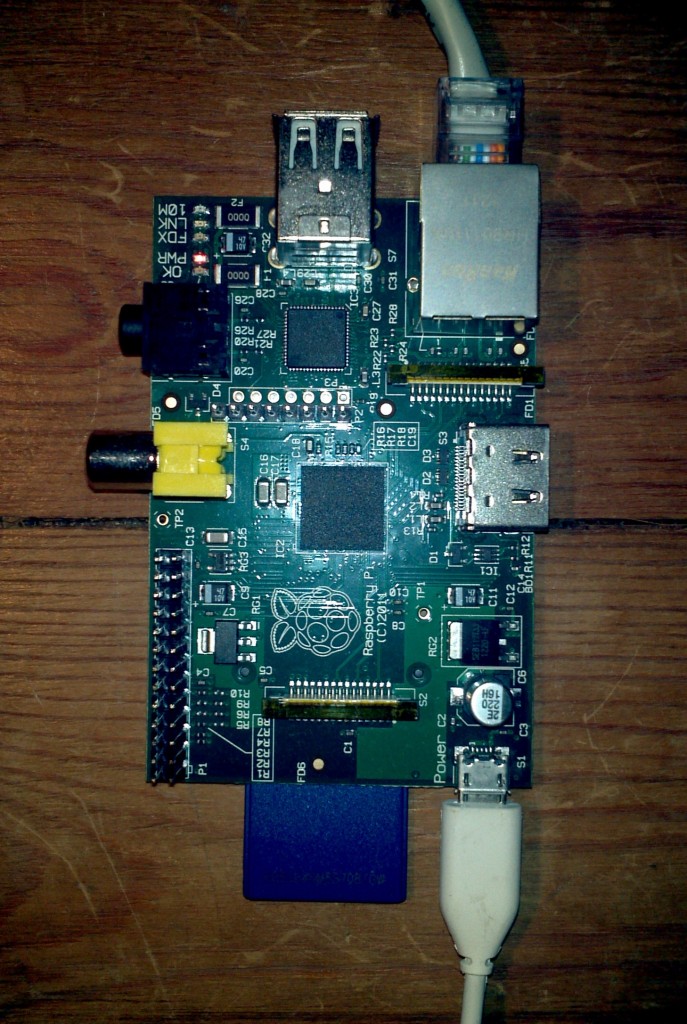
A Raspberry Pi model B, connected to the internet
Hence such a piece of electronics wouldn’t in and of itself add a whole lot to the price of an electric vehicle and/or a garage in Dunchideock, or anywhere else on the planet for that matter.
In conclusion, I also cannot help but wonder how much the Great Dunchideock Blackout cost Western Power Distribution, how much the evidently changing climate in this part of the world is costing and will cost them, and how their electricity distribution network is coping with the assorted stresses and strains generated by all the renewable power sources currently being tacked onto it down here in not so Sunny South West England that do not currently have any form of energy storage associated with them.